The Arab League Members
Introduction to the Arab League and its History
The Arab League, also known as the League of Arab States, is a regional organization that brings together 22 countries in the Middle East and North Africa. It was founded on March 22, 1945, in Cairo, Egypt, with the signing of its charter by six member states – Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia and Syria.
The main objective behind forming the Arab League was to promote unity and cooperation among its member states in various fields, including economic, political, and cultural spheres. The league aimed to strengthen ties between Arab nations and to defend their common interests.
History has played a significant role in shaping the formation of the Arab League. In the aftermath of World War I, we saw an increase in nationalist movements across the Middle East as countries under Ottoman rule sought independence. In response to this growing sense of nationalism and calls for pan-Arabism, King Faisal I of Iraq called for a conference to discuss a unified approach towards achieving independence from colonial powers.
This conference took place in 1920 and established an organization called "The General Syrian Congress". However, it failed to gain support from all Arab nations due to differing opinions on how best to achieve independence. It wasn't until after World War II that there was renewed interest in creating a united Arab front.
In September 1944, representatives from seven Arab countries met in Alexandria, Egypt, to discuss forming an alliance. This meeting led to another one held on March 13th,1945.
Understanding the Purpose and Goals of the Arab League
The Arab League, also known as the League of Arab States, is a regional organization that aims to promote cooperation and unity among its member countries. Established in 1945, the league has evolved over time and currently consists of 22 member states, spanning from North Africa to the Middle East.
One of the primary purposes of the Arab League is to foster political and economic collaboration among its members. This is achieved through regular meetings and conferences where leaders discuss trade, foreign policy, and cultural exchange. By working together, these countries aim to strengthen their positions on the global stage and enhance their influence in international affairs.
In addition to promoting cooperation, another key goal of the Arab League is to maintain peace and stability within the region. The league serves as a platform for member states to resolve conflicts peacefully rather than resorting to violence. It also advocates for human rights and social justice within its borders.
Another critical aspect of the Arab League's purpose is preserving the Arabic language and culture. As an organization representing predominantly Arabic-speaking countries with shared histories and traditions, it seeks to promote these cultural identities while embracing diversity among its members.
Moreover, one of the main objectives of the Arab League is to support economic development in its member states. It aims to boost economic growth and alleviate poverty within the region through initiatives such as joint investment projects and free trade agreements. This benefits individual countries and contributes towards greater regional stability by reducing socioeconomic disparities.
Overview of Member Countries and their Geographical Locations
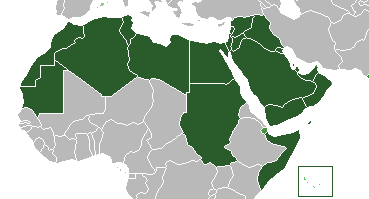
The Arab League is a regional organization comprising 22 member countries, all located in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. These countries are united by their language, history, and cultural heritage.
Geographically, the member countries of the Arab League cover a vast area stretching from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east. Most of these countries are situated on the Arabian Peninsula, while others are located in the Levant, North Africa, and some parts of Eastern Africa.
One interesting fact about the Arab League is that it includes landlocked and coastal countries. This diversity adds to its unique character and highlights different member states' varied landscapes and natural resources.
The Arab League is a regional organization comprising 22 member countries, each with its unique cultural, religious, and political landscape. Despite being united by a common language and shared history, the Arab League is home to diverse cultures, religions, and political beliefs. When you list the
Arab League Members
1. Iraq
2. Syria
3. Lebanon
4. Jordan
5. Saudi Arabia
6. Bahrain
7. Qatar
8. United Arab Emirates
9. Oman
10 Yemen
11 Kuwait
12 Egypt
13 Libya
14 Tunisia
15 Algeria
16 Morocco
17 Mauritania
18 Sudan
19 Somalia
20 Palestine
21 Djibouti
22 Komor
On a global scale, the Arab League represents avoice for over 400 million people in its member states.
Future Prospects for the Arab League
The Arab League has been a key player in the Middle East for over 75 years, promoting cooperation and unity among its member countries. As the region continues to undergo rapid changes and challenges, it is important to examine the future prospects of the Arab League and its role in shaping the destiny of its member nations.
One of the significant areas of focus for the Arab League in the coming years will be economic development. With a combined GDP of over $3 trillion, there is significant potential for growth and prosperity within the league's member countries. The league has already taken steps towards enhancing economic cooperation by establishing a free trade zone among member states and encouraging investment and trade among them. In addition, efforts are being made to reduce trade barriers and promote intra-Arab investments, further boosting regional economic integration.
Another key area that holds great promise for the future of the Arab League is political reform. Many member countries have been experiencing internal turmoil and unrest, leading to calls for political change. The league has supported democratic transitions in its member states, including monitoring elections and providing technical support for electoral processes. Moving forward, it will be crucial for the league to continue promoting political stability and good governance within its member nations.
In terms of security, several ongoing conflicts within the Arab world pose a threat to regional stability. The Syrian civil war, Yemeni crisis, and Libyan conflict are just some examples of these challenges that require urgent attention from both individual countries as well.