Middle East Euphrates River and Africa's Nile River Two Lifelines
The Euphrates River and the Nile River Comparing the Middle East's Lifelines
Introduction to the Middle East Euphrates and Africa's Nile River
The Middle East is home to two of the world's most renowned rivers - the Euphrates and the Nile. These ancient waterways have played a vital role in shaping the region's history, culture, and economy for thousands of years.
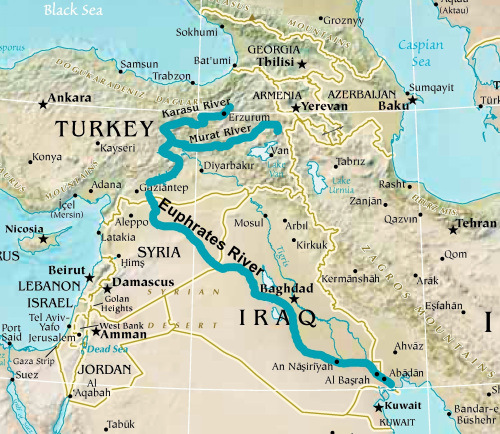
The Euphrates River is one of Western Asia's longest and most historically significant rivers. It originates from Turkey's eastern highlands and flows through Syria and Iraq before emptying into the Persian Gulf. The river spans over 2,715 kilometers (1,688 miles) in total length, making it comparable to other major rivers such as the Nile, Amazon, and Yangtze.
Since ancient times, civilizations have flourished along the banks of the Euphrates River due to its fertile floodplain. The river was crucial for agricultural development as it provided a reliable source of water for irrigation. This led to an abundance of crops, such as wheat, barley, dates, and cotton, which were traded with neighboring regions. The Mesopotamian civilization also emerged in this region around 5000 BCE when people began settling on its fertile banks.
In addition to its economic importance, the Euphrates holds great religious significance for three major religions - Christianity, Judaism, and Islam. According to Christian beliefs, it is believed that Adam and Eve lived near its banks after they were expelled from Eden. For Jews and Muslims alike, it holds a special place, as is mentioned numerous times in both their holy texts.
Moving on to Africa's longest river - The Nile River is approximately 6,650 kilometers (4,132 miles) long, stretching from Lake Victoria in Uganda all the way up north until it empties into the Mediterranean Sea near Egypt's capital city, Cairo. The Ancient Egyptians considered it a sacred river and called it "Ar or Aur," meaning black because of the fertile black soil left by its annual floods.
The Nile has been a crucial lifeline for Egyptian civilization as early as 5000 BCE. Its regular flooding provided rich silt, essential for agricultural production along its banks, leading to the development of advanced farming techniques such as irrigation and crop rotation. The river also served as a major transportation route, connecting Upper Egypt with Lower Egypt and facilitating trade within the region.
Both the Euphrates and Nile Rivers have played significant roles in shaping the Middle East's history, culture, and economy. These vital waterways continue to provide resources that sustain life in this region and are revered by many religions. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into their similarities and differences to better understand their importance to this part of the world.
Historical significance of the rivers in the Middle East
The Middle East is a region rich in history and culture, with its rivers playing a significant role in shaping the civilizations that have thrived there. Among the many rivers that flow through this region, two stand out as major lifelines - the Euphrates River and the Nile River. These two waterways are essential for sustaining life and hold great historical significance.
The Euphrates River has been referred to as the “cradle of civilization” due to its location and impact on Mesopotamian societies. It is one of the longest rivers in Western Asia, stretching over 1,700 miles from Turkey through Syria and Iraq before finally emptying into the Persian Gulf. The river was crucial for ancient civilizations such as Sumerians, Babylonians, Assyrians, and Persians, who established their empires along its banks.
One of the main reasons the Euphrates hold such historical importance is its role in agriculture. The fertile lands around it were ideal for farming crops like wheat, barley, and dates, which were vital in sustaining these early societies. The river also provided a source of transportation for trade routes between cities, making it an essential economic lifeline for these civilizations.
Moreover, several significant events and innovations are associated with this mighty river. It is believed that ancient Mesopotamian societies developed irrigation systems along its banks around the 6th century BC. This revolutionary technique allowed them to control floods and maximize agricultural production, ultimately leading to population growth and urban development.
Similarly, the Nile River holds immense historical significance for countries such as Egypt with its origin dating back over 30 million years ago. Stretching over 4,000 miles from East Africa through Sudan before flowing into Egypt's Mediterranean coast, it is known as the world's longest river.
One of the most notable contributions of this river was towards Ancient Egyptian civilization's prosperity from 3150 BC to 30 BC. The Nile's annual flooding resulted in the deposition of fertile silt, which was crucial for agriculture and allowed the Egyptians to develop a complex and sophisticated society.
The river also played a significant role in shaping Egyptian religion and culture. The ancient Egyptians believed that the Nile was a deity named Hapi, who was responsible for bringing life to their land through its floods. This belief is reflected in their religious practices, art, and architecture.
Both the Euphrates and Nile Rivers have played significant roles in shaping the history of Middle Eastern civilizations. These lifelines remain important even today, from providing sustenance through agriculture to serving as transportation routes and influencing cultural beliefs and practices.
Physical characteristics and geographical location of each river
While both rivers share similarities in their roles as lifelines for the surrounding communities, they also have distinct differences in terms of their physical characteristics and geographical locations.
Physical Characteristics:
The Euphrates River is approximately 2,800 kilometers long, making it one of the longest rivers in Western Asia. It originates from Turkey's Eastern Anatolia region and flows through Syria and Iraq before ultimately emptying into the Persian Gulf. The river is known for its fast-flowing currents, with an average speed of 3 meters per second, making it ideal for irrigation and transportation purposes.
On the other hand, the Nile River stretches over 6,600 kilometers, making it one of the longest rivers globally. It has two main tributaries – the White Nile that originates from Lake Victoria in Uganda and the Blue Nile from Ethiopia – which merge near Khartoum to form one mighty river that flows through Sudan and Egypt before draining into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is renowned for its slow-moving currents compared to other major rivers worldwide.
Geographical Location:
The Euphrates River runs through three countries: Turkey, Syria, and Iraq. Its upper course flows through mountainous terrain with steep valleys, while its lower course passes through a flat desert landscape. Its location has made it essential for trade routes since ancient times, as well as a vital source of water for agricultural activities in these arid regions.
In contrast, the Nile River runs through eleven countries but plays a significant role mainly in Egypt and Sudan due to its impact on agriculture. Most notably, it provides water for irrigation along its banks that support nearly all of Egypt's crops. Moreover, it serves as a primary transportation route connecting cities along its banks.
Unique Characteristics:
Aside from their physical features and geographical locations, each river also has unique characteristics that set them apart. The Euphrates River is known for its high salinity levels, making it challenging to use for human consumption. However, this same characteristic has made the river a haven for certain species of fish and birds.
The Nile River, on the other hand, is famous for its annual flooding cycle caused by heavy rainfall in the Ethiopian Highlands. This flood brings fertile silt and minerals that enrich the soil along its banks, making it ideal for farming. This natural phenomenon has been vital in sustaining ancient civilizations such as the Pharaohs' civilization in Egypt.
Importance of the rivers in terms of agriculture and economy
The importance of these rivers can be further highlighted by looking at some key economic indicators, such as employment generation. Agriculture alone accounts for over 25% of employment opportunities in Egypt while contributing around 14% towards Iraq's GDP – both directly linked to river-dependent farming practices. The availability of water from these sources enables farmers to diversify their crops beyond traditional grains such as wheat or rice into high-value products like fruits, vegetables, dairy products, etc., resulting in increased income levels.
Additionally, hydropower generated from dams built along these rivers provides electricity essential for running industries that contribute substantially towards gross domestic product (GDP). For instance, hydropower makes up almost 90% of Sudan's total energy production while accounting for over half of Ethiopia's total electricity supply – all thanks to its position along the Nile River.
Furthermore, tourism is another sector that benefits from these lifelines, with the Nile being a popular attraction for cruises and river tours. These activities bring in foreign exchange earnings that aid in boosting the economy while also providing job opportunities for local communities.
It is evident that the Nile and Euphrates rivers are crucial lifelines that play a vital role in sustaining agriculture and driving economic growth in the Middle East. Their significance goes beyond just providing water for irrigation but extends to various other sectors, making them integral to the region's development and prosperity.
Human impact on the rivers and their ecosystems
Human impact on rivers and their ecosystems is a major concern in the Middle East, where the Euphrates River and Nile River play vital roles in providing water for agriculture, drinking, and other activities. The human population in this region has been steadily increasing over the years, leading to a significant increase in demand for water resources.
Nile River
One of the most significant impacts of human activity on rivers is pollution. Industrial and agricultural activities along the banks of both the Euphrates and Nile Rivers have led to increased levels of pollution from chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and other harmful substances. This pollution affects water quality and poses a threat to aquatic life and other species that depend on these rivers for survival.
Another major issue facing these rivers is overexploitation. Due to growing populations and agricultural needs, there has been an increased demand for water from both the Euphrates and Nile Rivers. As a result, water extraction has exceeded the natural replenishment rate, leading to decreased river flow and drying up of certain areas along their banks. This has not only affected the availability of freshwater for humans but also posed a threat to aquatic habitats.
The construction of dams along these rivers has also significantly impacted their ecosystems. While dams can provide hydropower and regulate river flow for irrigation purposes, they also disrupt natural river processes such as sediment transport, essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems. Furthermore, dam construction can lead to the displacement of communities living along these rivers' banks as well as cause changes in downstream water availability.
Deforestation is another factor contributing to human impact on these rivers' ecosystems. Trees play a crucial role in regulating river flow by reducing soil erosion which helps maintain sediment load necessary for aquatic habitats' health. However, deforestation due to urbanization or clearing land for agriculture leads to increased soil erosion, negatively impacting river ecosystems' health.
Moreover, climate change is also a significant factor affecting the Euphrates and Nile Rivers. The region has been experiencing prolonged droughts and extreme weather events, leading to decreased water levels in these rivers. This affects water availability for human use and poses a threat to the diverse range of species that depend on these rivers for survival.
Human impact on rivers such as the Euphrates and the Nile is multifaceted and can have severe consequences on their ecosystems. It is crucial for governments and communities to take proactive measures to address these issues through sustainable practices such as implementing stricter pollution regulations, promoting responsible use of water resources, and preserving natural habitats along these lifelines. Preserving these rivers' health is vital for the environment and sustaining the livelihoods of millions of people who rely on them.